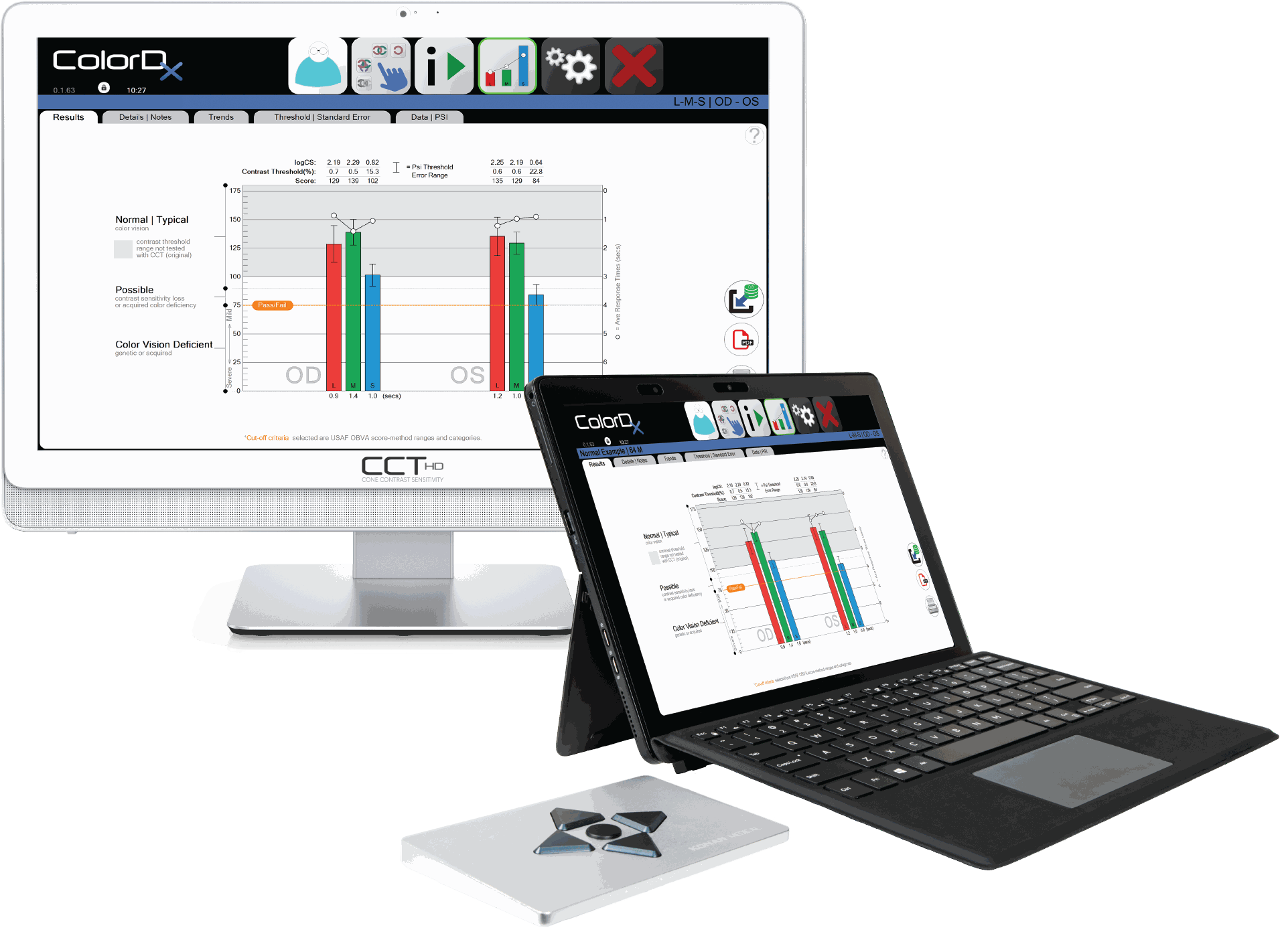
ColorDx® CCT HD®
Frequently Asked Questions &
Specifications
Frequently Asked Questions
A. It depends. Not all color vision tests are classified as an “Extended” type. Extended color vision testing is described under CPT code 92283 as a psychophysical test of visual function. Deficiencies and changes in perception of color are ideally tested monocularly and are a summation of function from the visual pathway, optic nerve, and retina, especially the macula with the highest density of cone receptors.
An example of detailed description of procedures, indications, and coding, documentation, and indication guidelines may be found at Decision-Maker Plus.
Importantly, it should be noted that pseudoisochomatic tests (or “PIP” tests), whether printed or digitally presented, are specifically excluded from the definition of an “extended color vision” with 92283 as “color vision testing with pseudoisochromatic plates (such as HRR, Ishihara, and others) is not reported separately but included in the appropriate general or ophthalmological service”.
Fraunfelder, Fraunfelder, Chambers. Clinical Ocular Toxicology. Sanders Elsevier, 2008: 320Yes. With increasing age, acquired color deficiencies become more common and can be an important sign accompanying many diseases, toxicity or side affects of many drugs and substances prescribed or used day-to-day. This important sign is frequently not tested even though a color test is administrated as common printed color vision test do not test blue type (S-cone) deficiencies (Ishihara color tests are an example of tests that do not have blue / S-cone testing features)
Different from genetic types that are quite stable through life, acquired deficiencies vary over time, are conditioned on the cause, and can progress to to severe monochromatic colorblindness. A person can have both genetic and acquired deficiencies.
There are broad categories of condtions that may lead to acquired color deficiencies:
-
Trauma
-
Medications
-
Diseases
-
Toxic Chemicals
-
Age
Children:
All children should have their color vision tested before starting school, ideally in pre-school. The most common deficiencies found are typically genetic and are approximately 10 times more common in males.
Teens and Young Adults:
Persons who are considering occupations or professions for the future where normal color vision is needed or required should be assessed to enhance career decisions for both job performance and safety. Examples are pilots, navigators, air traffic controllers, school bus drivers, some law enforcement personnel, electricians, electronic technicians, railroad conductors, medical technologists, and dental lab technicians. Genetic deficiencies that have not been well screened while young can be a real help in formulating a successful career. Acquired deficiencies are less common during younger years.
Older Adults and Seniors:
As we age, there are multiple pathways and combinations to acquired color deficiencies that can be valuable as diagnostic points. Examples are many diseases (diabetes, MS, and glaucoma), common aging changes such as cataracts, and hundreds of pharmaceuticals, products, and substances commonly used or prescribed. Examples of the many substances affecting color vision can be toxicity from alcohol, aspirin, herbal medicines, ibuprofin, and prednisone, and marijuana. The newest electronic color vision diagnostics that are highly sensitive and specific provide physicians with a new diagnostic tool that may also be helpful for easily assessing changes over time that was not possible with historically used printed color test books. Konan’s ColorDx CCT HD is an example of a comprehensive color vision diagnostic test that also includes trends analysis with standard errors to better understand changes over time with scalar measured values. Both genetic and aquired color deficiencies may be present simultaneously and are individually detected and quantified with the CCT HD test
-
Genetic color vision deficiencies are found in approx:
-
-
8% of males, more common
-
0.5% of females, less common
-
-
Most color perception problems are color vision “deficiencies” rather than color “blindness”
-
Protan type deficiencies are reduced sensitivity to red from “L-cones”. Genetically, reduced L-cone function may be due to the peak sensitivity of L-cones being closer than normal to the peak sensitivity of M-cones, and is referred to as “Protanomoly”. An absence of L-cones is the severe form, “Protan”.
-
Deutan type deficiencies are reduced sensitivity to green from “M-cones”. Genetically, reduced M-cone function may be due to the peak sensitivity of M-cones being closer than normal to the peak sensitivity of L-cones, and is referred to as “Deutanomoly”. An absence of L-cones is the severe form, “Deutan”.
-
Tritan type deficiencies are reduced sensitivity to blue from “S-cones”
-
Both Protan and Deutan deficiencies confuse red and green colors as being similar
-
Protan and Deutan deficiencies are typically genetically inherited but may also be acquired
-
Tritan type deficiencies are typically acquired and may be more common than genetic types
-
Most color deficient people see colors, but have some colors that appear the same
-
Most common printed color vision tests are pseudo-isochromatic or “PIP” plates and may not test for S-cone type acquired color vision deficiencies
Women can also be color deficient, although with genetic deficiencies, only about one-tenth as frequently as men. About 8% of men and 0.5% of women have genetic color vision deficiencies, of which most are simple, recessive traits as red-green deficiencies due to “sex-linked” X chromosomes. Men are mainly affected as women have two X chromosomes and men have an X and a Y chromosome. If a man’s one X chromosome is defective, he will be color deficient, whereas a both of a woman’s chromosomes would need to have this trait in order to have color deficiency (“colorblind”).
Acquired color deficiencies are likely to be the most common type of deficiency with women occuring generally equally in both genders and more prevelent with age.
The vast majority of color deficient persons see the world in color too, but common color-differentiated situations may provide challenging consequences not well appreciated by color normal individuals. Following are examples of how common types of color vision deficiencies affect those persons in day-to-day circumstances.
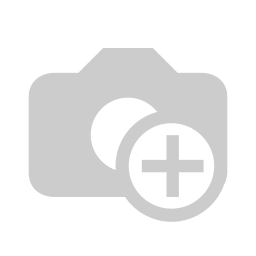 An illustration of Deutan color deficiency and normal color vision
An illustration of Deutan color deficiency and normal color vision
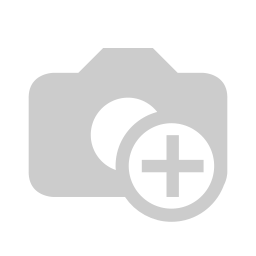 An illustration of Deutan color deficiency and normal color vision
An illustration of Deutan color deficiency and normal color vision
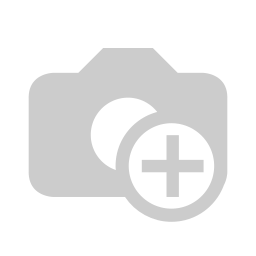 An illustration of Protan color deficiency and normal color vision
An illustration of Protan color deficiency and normal color vision
 An illustration of Deutan color deficiency and normal color vision
An illustration of Deutan color deficiency and normal color vision
 An illustration of Protan color deficiency and normal color vision
An illustration of Protan color deficiency and normal color vision
 An illustration of Tritan color deficiency and normal color vision
An illustration of Tritan color deficiency and normal color vision
Dr. Shinobu Ishihara first published his pseudo-isochromatic plate, “PIP”, method in 1917 for red-green color deficiency testing for the Japanese railroad industry. The ColorDx pseudo-isochromatic tests “PIP plates”, both digital and printed versions, marketed by Konan were discontinued in January 2018 after 5 years in the marketplace. 
Pseudo-isochromatic color vision testing has historically played an important role in assessment of color vision testing for about 150 years, primarily used for for screening to identify the presence of genetic “colorblindness”. Ishihara plates, first hand watercolor painted in the early 1900’s, still are used clinically today.
The United States Air Force approached Konan Medical in 2014 to collaborate on the development of the next generation color vision diagnostic product using a contemporary “cone-isolation, contrast sensitivity” strategy. This state-of-the-art system includes expanded low contrast testing ranges, significantly higher granularity, and a robust Bayesian threshold method. The result of this research and development is ColorDx CCT-HD*. As CCT-HD was introduced into the market, Konan also terminated its distribution of the pseudo-isochromatic products near the end of 2017, focusing exclusively on CCT-HD, which has been called the world’s finest high-fidelity test of color vision function.
Konan’s pseudo-isochromatic product customers may contact sales@konanmedical.com to receive a limited-time trade-up offer from the discontinued ColorDx pseudo-isochromatic products.
*CCT-HD developed in collaboration with the US Air Force, School of Aerospace Medicine, Operational Based Vision Assessment Team under CRADA (Creative Research and Development Agreement).
Specifications
| Fundamental Method | Cone-isolation Contrast Sensitivity |
| Co-development with US Air Force | Creative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) with USAF School of Aerospace Medicine, OBVA Team |
| Laptop Computer |
Dell Latitude 7320 13.3" FHD (1920x1080) AG, Non-Touch, WVA, 250 nits, HD RGB Camera+ Mic, WLAN. Windows 10 Pro English, French, Spanish | i5-1145G7 vPro, Intel Iris XE Graphics 8GB Memory. 11th Generation Intel Core i5-1145G7 (4 Core, 8M cache, base 2.6GHz, up to 4.4GHz, vPro). M.2 256GB PCIe NVMe Class 40 Solid State Drive. |
| 4-button response pad | Konan exclusive USB answer interface eliminates letter recognition problems and hunt and peck on a keyboard or mouse |
| USB Colorimeter | OEM i1Pro with built-in fast system color verification and automated calibration |
| Reporting |
On-screen PDF to network printer PDF to network EMR location |
| Testing Options | All cones, individual L, M, S cones or any combination; Monocular or binocular; Adaptive or Full Threshold; user selected test distances with dynamic optotype sizing; Tone feedback options |
| Patient Instructions and interactive demo widget | Available in multiple languages, illustrated patient instruction page includes an interactive demo to assure instructions are understood and demonstrated proficiency prior to testing including auditory feedback as "correct" tone or "miss" tone |
| Trends Analysis | Detailed trending over time by eye, by isolated cone |
| Psi Threshold | Robust, academic-based Bayesian threshold method with on-screen reporting of Standard Error estimations by response |
| Adaptive Testing | RUser-selected adaptive test seamlessly reduces test time for subjects with low standard error score |
| Achromatic Contrast Sensitivity | Contrast sensitivity reported at 4 contrast levels, and AUC indicative of overall functional vision |
| Monocular and binocular | User selected administration of tests OD and OS or OU |
| Response tones | Clear, language-independent response feedback, as high (correct) - low (incorrect) tones, or operator selected high tone only, and no auditory feedback |
| Response-time reporting | Expressly with the 4-button response pad, patient difficulty in answering is assessed as a separate measure |
| Regulatory | FDA Listed | CE | TGA | Available in Canada |
